Title
MARATHON – MAnagement of Radio Access neTwork slicing witH multi-applicatiON concurrency
MARATHON Tutorial: http://wiki.5ginfire.eu/experiments/marathon_upc
Organization
Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC), Spain https://www.upc.edu
Experiment description
The main goal of the MARATHON experiment has been the design and development of a Radio Slicing Management Function (RSMF) intended to extend the WINS_5G platform with new radio slicing management capabilities by leveraging the HyDRA technology. This enables the flexible and dynamic provisioning of network slices of the radio access part, denoted in the following as radio slices (RSs), according to users and applications’ requirements, and the enforcement of different strategies with regard to how radio resources are allocated to the RSs based on the desired trade-off between spectrum efficiency and level of isolation between the slices.
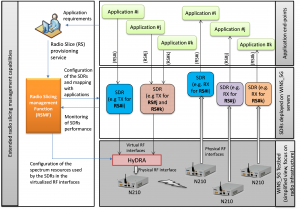
The experiment framework envisioned in MARATHON is illustrated in Figure 1, showing the role of the new RSMF component brought into the WINS_5G platform and the relation with HyDRA. As illustrated in the figure, the HyDRA technology enables N210 USRPs to support multiple Software Defined Radio (SDR) applications simultaneously, ensuring isolation and allowing each SDR application to adopt its own PHY and MAC technology. On this basis, the new RSMF component brought by MARATHON offers a RS provisioning service to the end-users and relies on the use of templates for the characterisation of the expected RS behaviour as requested by the end-users and applications. With such information, the RSMF component carries out the proper configuration of both the SDRs that will handle applications’ traffic and the HyDRA component of the WINS_5G platform.
As an example of a potential configuration of the RSs that can be realised in such a framework, Figure 1 illustrates the case that traffic from application #i is decided to be handled through RS#i, which is implemented using SDR components for transmission and reception that are not shared with other RSs. On the other hand, traffic from applications #j and #k is decided to be handled through, respectively, RS#j and RS#k, which now rely on the use of a shared SDR transmission component with traffic differentiation features (e.g. slice-aware packet scheduling features). Also of note is that the two SDR components illustrated in Figure 1 for the implementation of the transmission part of all the RSs are actually sharing the same USRP device as facilitated by the use of the virtual RF interfaces exposed by the HyDRA component.
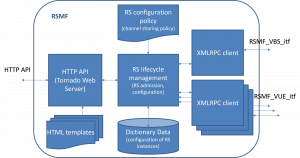
Figure 2 illustrates the functional architecture of the implemented RSMF component. Internally, the core of the RSMF component is a processing engine, named as RS lifecycle management (RS LCM) function, in charge of the decision-making logic for the creation and configuration of the Radio Slice Instances (RSIs). The RS LCM engine is written in Python. The parameters of the activated RSIs are stored in a repository built using a Dictionary, which is a dynamic list for data storage. The operation of the RS LCM engine is dictated by the RS configuration policy, which establishes the channel sharing policy between RSIs and Hydra radio slices.
The interaction of the RS LCM function with the consumer of the RS provisioning service is realized via an HTTP API. This is the interface used to expose the RS provisioning services to the MARATHON experimenter. It allows for the allocation, modification and deallocation of RSs. RS provisioning services can be accessed from a conventional web browser (e.g. Chrome, Firefox).
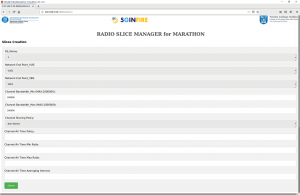
An illustration of the implemented GUI for the RS provisioning service is given in Figure 3, showing the HTML form used to populate the RS Template (RST) attributes used to request the creation of a RS.
Conclusion
In order to investigate the practical implementation and management of network slicing in 5G systems, focusing in the radio access part, the MARATHON experiment has exploited the Hypervisor for Software Defined Radios (HyDRA) technology for Universal Software Radio Peripherals (USRPs) virtualisation provided within the Wireless Network Slicing Functionality for 5G (WINS_5G) platform at Trinity College Dublin (TCD).
The MARATHON experiment has delivered a new Radio Slicing Management Function (RSMF) component that extends the WINS_5G platform with radio slicing management capabilities. The new component leverages the HyDRA technology included within the WINS_5G and allows for the dynamic creation, modification and release of radio slices (RSs). NS and VNF descriptors have been produced to allow the instantiation of the experiment through the OSM servers of the 5GinFIRE portal, using the developed image, VNFs and NS.
The RSMF provides a tool for future researchers to experiment with the management of RSs as part of the whole network slicing functionality. The developed RSMF allows testing different radio resources allocation strategies like fixed or flexible radio channelization per RS.